Aquaponics Projects For Beginners
Aquaponics 4 You
Aquaponics is a complete beginners guide to learn how to harness the power of both fish and plants. The waste products that fish produce are food for the plants, so that your plants can grow twice as fast as normal plants. Not only will the grow faster, they will also produce 10 times more than the average garden will ever dream of. And you don't ever have to weed! This is a 100% organic way to grow your own food. The Aquaponics guide comes in PDF format and gives you access to easy step-by-step videos to learn to set up your own garden. The book gives you the tools to build a small home garden or a multi-acre farming operation. What you do with the information is up to you! Not only does the complete instruction course come with everything you need to get started, it includes six extra books that cover organic gardening, flower gardening, organic farming, worm farms, cooking organically, and eating healthy. Don't waste your time on a small garden that needs weeding and constant care. Use Aquaponics to grow your best garden every.More here...
Contents: Ebook
Author: John Fay
Official Website:www.aquaponics4you.com
Price: $27.00
Aquaponics 4 You Review

It is pricier than all the other ebooks out there, but it is produced by a true expert and includes a bundle of useful tools.
我认为电子书是,如果你没有this e-book in your collection, your collection is incomplete. I have no regrets for purchasing this.
Read full review...DIY Aquaponics Made Easy
This program is equipped with a various step-by-step guide, video tutorials and user manuals to help you discover how you can easily build your own aquaponics system in your backyard. The good thing about this program is that you will be able to grow ten times tasty and healthy organic produce in the same space. In addition to that, with the aquaponics system, watering plants is no longer a problem because you get to use 90 percent less water and also save 70 percent on electricity. From this, you can already tell that this system is very affordable and manageable as compared to the normal way of planting crops. When planting the traditional way, you need to bend, you need soil and weeding is also required. This is always to ensure that the plants are growing in a conducive environment. However, the disadvantage is that after planting, you tend to have back pains which can worsen and cause health problems. The good news is that with the aquaponics system, you do not need soil, no weeding is required and above all, you will not need to bend when planting, meaning that you can say goodbye to back pains.More here...
DIY Aquaponics Made EasySummary
Contents: User Manuals, Video Tutorials, Routine Checklist
Author: Steven Fu
Official Website:diyaquaponics4you.com
Aquaponics 4 Idiots
The aquaponics for idiots system is designed to guarantee you a breakthrough in growing you up to ten times the normal amount of plants for your plants. You can conduct these processes quickly, yet the plants will be much healthier while the fish do all the work for you. As you go through the guide, you will discover that this particular system does not require you to do the normal weeding, deal with soil pests, engage in spreading of fertilizer or compost, and irrigate your plants. Intense research carried out by the creator over time results in a development system easily built in the backyard or even in a large-scale commercial center. This process is possible; it depends on your needs and how fast you would like to generate cash. In the end, you will have access to so many plants and fish that you can sell in the local market to inject additional income for you and your family. Some of the benefits of using this particular system include the fact that you will use less energy than conventional gardening, have access to multiple sources of income, and no more wedding or soil work. Additionally, you get to enjoy up to times the average number of plants.More here...
Aquaponics 4 IdiotsSummary
Contents: EBook
Author: Sam Adams
Official Website:www.aquaponics4idiots.com
Price: $37.00
How To DIY Aquaponics
本产品只作为一个作家的identified to the users as Simon. The program is supposed to help you produce vegetables and fruits or fish with the least amount of time you can imagine. It works in a way that balances nature by applying the concept of oxygen circle trees provide us with oxygen to breathe, we breathe out carbon dioxide, and in turn, the trees breathe the carbon dioxide we exhale and breathe out oxygen. Because of this, the system is automatic and you don't have to think about where and how the plants sustain themselves. With this system, the food supply can be automated by combining hydroponics and aquaculture to form aquaponics. Aquaculture is the process of growing fish in a tank. This process produces a lot of ammonia, minerals, algae, and other by-products that, without filtering them out, could harm the fish. And that is where the plants come in. Plants eat the minerals, ammonia, algae, and nitrates as well as other by-products of the aquaculture process. This product consists of instructions that can help you connect the fish tank water to the water of the hydroponics system. This way, your plants get an automatic food supply of almost everything they need to grow from the fish water, and in turn, the plants filter the water for the fish. In the end, it is a win-win situation for the fish and plants and a double win for you as you will be getting healthy fish and plants for food.More here...
How To DIY AquaponicsSummary
Contents: Ebooks
Author: Simon
Official Website:www.howtodiyaquaponics.com
Price: $37.00
Climate Change Impacts on Fisheries and Aquaculture Are Less Well Understood
Aquaculture is growing rapidly in the United States and elsewhere as the availability of wild seafood declines. Impacts of climate change on aquaculture are not well studied, but ocean acidification and the difficulty of moving aquaculture infrastructure to new locations as fish habitats shift may pose significant challenges to aquaculture production.
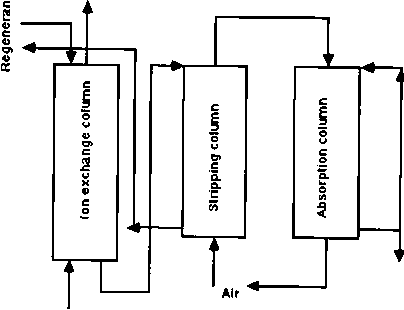
Application of Ion Exchange
Many industries discharge waste water with high concentrations of ammonium, as referred to in Section 7.6. Ion exchange is, however, not a very attractive treatment method for removal of high ammonium concentrations, because the regeneration becomes more frequent and the operation costs are very dependent on the elution frequency. Asair strippingbecomes more attractive the higher the concentration of ammonium is, these types ofindustrial wastewaters are probably better treated by biological methods or by air stripping at least from an economic's point of view. Ion exchange is an attractive method particularly for concentrations up to 100 mg l (Haralambous et al, 1992) and for waste water anddrinking water, which do not contain sufficient organics to allow a biological treatment. Ion exchange has furthermore been applied for removal of ammonium from water inrecyclingaquaculture plants.
Land Treatment Systems
There are two major categories of reuse of wastewater, which have been practiced throughout the world potable use and nonpotable use. The potable use of wastewater mainly includes injecting reclaimed water to thedrinking watersupply after multiple levels of treatments, or using natural systems (including land applications) to treat wastewater directly. Nonpotableuses of wastewaterare many direct irrigation of agriculture fields usingfood wastewaterwith low BOD5 and TSS irrigation of parks, forests, or golf courses with low-load wastewater and use for aquaculture are the most promising examples. In many areas of the world, wastewater reuse has been practiced using a combination of treatment technologies that achieve a very high degree of treatment. Many states in the western U.S. have, over the past 20 years, been treating wastewater totertiary treatmentstandards and then allowing the wastewater to be reused for irrigation or for recharge to groundwater aquifers.
Phytoplankton increased reflectance
Gower et al. suggest that the MERIS 709 nm band provides an important tool for the detection of intense algal blooms, phenomena of great significance - because they are so often toxic -for aquaculture. In a later study, Gower et al. (2008) report that with this technique they find an average of about one plankton bloom event somewhere in the world on any given day.
Types of Freshwater Ecosystem Services
Benthicorganisms in lakesand rivers provide food production mostly through the dependence of fish production on invertebrate prey and nutrient cycling. Globally about 8 X 106 tons of freshwater fish are harvested, with double that amount produced by aquaculture (FAO 1995). Productivity of these fisheries will, in part, depend upon benthic production directly (e.g., consumption of benthic invertebrates or aquatic plants) or indirectly (e.g., benthic mineralization of nutrients). For Beavers play an important role in wetland landscapes asecosystem engineers, creating a tremendous expansion of wetlands that otherwise would not have existed. Beaver harvests have averaged 400,000 pelts per year over the past century in North America (Novak et al. 1987). Alligators are also harvested for their pelts and meat, generating over US 16 million in a single year in the state of Louisiana, USA (Mitsch & Gosselink 2000).
Nutrient Cycling and Productivity of Lakes Lake Mendota Wisconsin United States
These integrative studies led to new questions about how management can enhance ecosystem services in freshwater bodies How are distinct ecosystems, with apparently clearly defined surface boundaries (e.g., small ponds, large lakes, and rivers), interconnected hydrologically over time and space How might these linked ecosystems function and affect each other in predictable ways Why must fisheries biologists addfertilizersto increase fish production in some locations (hatcheries, aquaculture ponds) when water-quality engineersare designing treatment plants to remove nutrients in other downstream locations (groundwaters, rivers, and lakes) Is production of fish for food versus recreation a necessary trade-off Or can aquatic ecosystems be managed to optimize complex production functions Can natural processes of nutrient cycling and organic-matter breakdown provide supplemental services that could save construction of new treatment plants Answers to such questions have emphasized that...
Estuarine and Continental Shelf Sediments
Although estuarine sediments contain few species relative to most other sedimentary habitats, they nonetheless represent hotspots for ecosystem processes that can extend well beyond the estuarine sediments. Of the ecosystem goods and services associated with shelf and nearshore ocean areas, people are most aware of provisioning of food (e.g., fish and shellfish), which has huge commercial and cultural importance in coastal societies worldwide. Even aquaculture businesses often rely on wild (natural) fisheries (e.g., for fishmeal) or natural supply of food (e.g., phytoplankton) for aquaculture species and, in some cases, for provision of brood and juvenile stocks. Marine plants are used as food, particularly in Asia, and seaweed extracts such as alginates and other phycocolloids are used in many industrial and food applications (e.g., manufacture of films, rubber, linoleum, cosmetics, paints, cheeses, lotions).
Global water use trends Ever increasing
Water use in agriculture, whether for livestock husbandry, aquaculture or crop production, has also affected water quality. Soil erosion, salinization, sedimentation, and nutrient and pesticide pollution have contributed to a decline in water quality in many of the world's river systems and coastal zones.
Current sensitivityvulnerability
世界上很少的海岸线现在超出了我nfluence of human pressures, although not all coasts are inhabited (Buddemeier et al., 2002). Utilisation of the coast increased dramatically during the 20th century, a trend that seems certain to continue through the 21st century (Section 6.3.1). Coastal population growth in many of the world's deltas,barrier islandsand estuaries has led to widespread conversion of natural coastal landscapes to agriculture, aquaculture, silviculture, as well as industrial and residential uses (Valiela, 2006). It has been estimated that 23 of the world's population lives both within 100 km distance of the coast and
Species biodiversity and conservation
What are the circumstances that could have driven the increased emphasis on species Are there different scientific networks involved in the ACIA than are involved with the IPCC Or could the context ofthe Arctic Councilhave created a stronger emphasis on these issues than the IPCC One observation is that the emphasis on species is particularly strong in Chapter 7. Arctic Tundra andPolar DesertEcosystems and Chapter 10. Principles of Conserving the Arctic's Biodiversity. These are also the two chapters that explicitly discuss biodiversity, followed by Chapter 8. Freshwater Ecosystems and Aquaculture, which also scores high on biodiversity. At a rather late stage in the ACIA process the concern raised that biodiversity issues were not treated enough in the
Fish farm lice annihilate BC's wild salmon
The findings add to evidence that raising salmon and other fish in ocean pens, banned from Alaska and controversial in the Pacific Northwest, can cause environmental damage and spread nonindigenous stocks, disease or parasites into wild populations. The study has already garnered extensive coverage by media, especially in Canada, and detailed critiques from the aquaculture industry and some academics. According to experts, the study also raises serious concerns about large-scale proposals for net pen aquaculture of other species and the potential for pathogen transfer to wild populations. This paper is really about a lot more than salmon, says Hilborn. It is about the impacts of net pen aquaculture on wild fish. This is the first study where we can evaluate these interactions and it certainly raises serious concerns about proposed aquaculture for other species such as cod, halibut and sablefish. In a May 16, 2007 provincial government report, the B.C.
Poverty And Ecocide
Geared mainly to producing for foreign markets.23 Indeed, the blue revolution of aquaculture, and in particular prawn farming in countries such as the Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Ecuador, and Mexico, reveals the devastating environmental impact of debt-driven, export-oriented production. Not only has the creation of prawn farms to service the Japanese, US, and European markets entailed the destruction of mangroves and associated coastal breeding grounds for fish, it has also disrupted traditional agriculture. The inflow of salt water due to the elimination of mangroves threatens to lower productivity of adjacent rice fields. The high demand for fresh water leaves little of this most precious resource for rice farming. In some areas, water supplies have dropped precipitously, prompting local authorities to ration it.24
Stabilization Ponds
One of the ancient wastewater treatment technologies, the stabilization pond (also referred to asa lagoon), has been used continuously as a method of sewage disposal. In some cases, these ponds were also utilized for aquaculture. Stabilization ponds are used for both municipal waste-water treatmentandindustrial wastewater treatment, particularly for wastewaters from small communities and seasonal industrial wastewaters as well as less affluent communities throughout the world (Fig. 6.1). Although stabilization ponds can be used in most regions of human habitation, their performances in treating wastes are at best in warm climates with adequate sunlight. The current interest inwaste stabilization ponds(wsp)is a result of the accidental discovery of their capabilities when WSPs were used initially as simple sedimentation basins or emergence holding ponds at wastewater treatment plants.
Economic Uses
Paper and textiles) as well as Epsom salts (MgSO4 7H2 O - agricultural and medicinal uses). Glycerol (used in dynamite and light industry) and p-carotene (used in food and medical industries) are both derived from Dunaliella, a green alga widely present insaline lakes. p-carotene is also derived from the salt tolerant cyanobacteria Spirulina. Finally, Artemia cysts, used as food materials for aquaculture (shrimp, fish, and crabs), are harvested commercially from saline lakes.
Removal of BOD
Because algae are difficult to remove and can represent an unacceptable level of suspended solids in the effluent, some pond and aquaculture processes utilize mechanical aeration as the oxygen source. In partially mixed aerated ponds, the increased depth of the pond and the partial mixing of the somewhat turbid contents limit the development of algae as compared to afacultative pond. Mostwetland systems(Chapters 6 and 7) restrict algae growth, as the vegetation limits the penetration of light to the water column.
Industrial Subsector
The industrial subsector is characterized by a purse seine fleet of about 750 vessels with an average capacity of 225 metric tons, employing about 26,000 fishermen and plant workers. Most of these vessels target small pelagic species (primarily anchovy), of which more than 90 is processed into fishmeal, a flourlike substance high in protein that is then used throughout the world primarily as an animal feed supplement and in aquaculture farming. The majority of nonmanagement laborers are fishing fleet, fishmeal plant, and cannery workers. A significant number also work in associated industries such as net making and repair, engine repair, and shipping services. Most of the women employed in this industry work in the canneries. Throughout the period of commercial fishing, the industrial subsector has wielded strong political influence through lobbying activities and through explicit places at the table within the policy-making process.